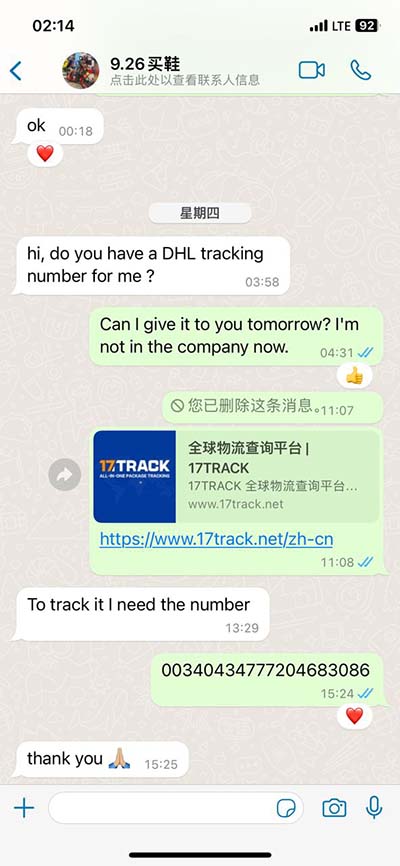
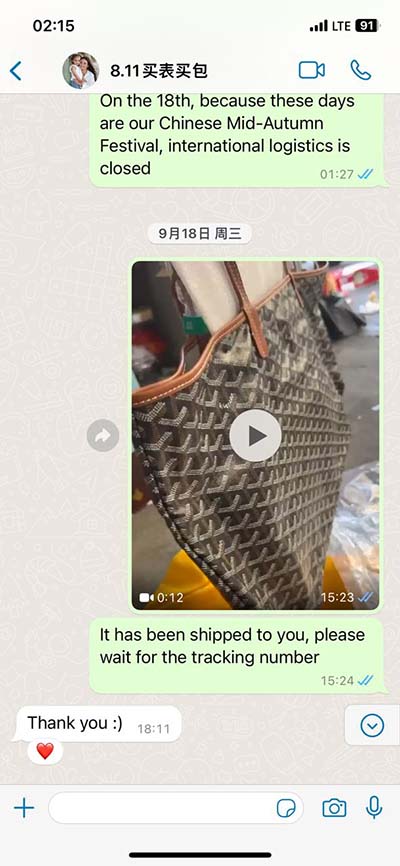
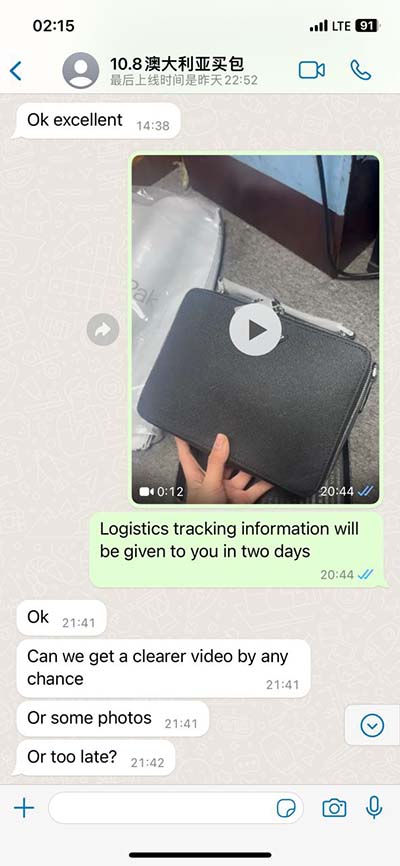
lv ejection fraction 55 | mildly reduced Lv systolic function lv ejection fraction 55 40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure.
$12K+
0 · reduced left ventricular systolic function
1 · mildly reduced Lv systolic function
2 · low normal Lv systolic function
3 · ejection fraction echo 55 60
4 · ejection fraction 50 55
5 · borderline low Lv systolic function
6 · borderline left ventricular ejection fraction
7 · Lv ejection fraction normal range
Order now with just a few clicks. Discover all the watches of the Seamaster Diver .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) Ejection fraction typically refers to the left . A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart.
40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure. Many doctors consider a normal ejection fraction to be 55%-75%. If yours is 50% or lower, it's a sign that your heart--usually your left ventricle--may not pump out enough blood. There's a gray.
For an ejection fraction in the range of 50% to 55%, most of the commonly used tests, if carefully performed, are accurate within a few percentage points (e.g. 55% plus or minus 3%). With respect to the lower limit of “normal” LVEF, it is important to remember that even at rest, the LV pumps a slightly different amount of blood in every beat.
In general LVEF ≥ 55% is considered “normal” by guidelines, with a low normal designation for LVEF 50-55%. We assess the prognosis of participants with low normal LVEF in the Multi Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. All participants were asymptomatic and had no known clinical CVD at baseline. Methods and Results. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).
reduced left ventricular systolic function
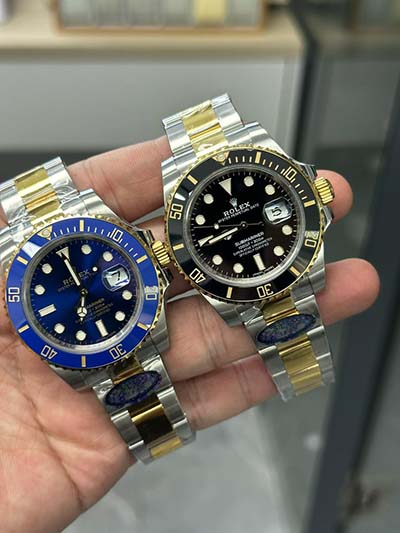
dainese rossi replica boots
In Conclusion. A normal ejection fraction of 55 to 65% is considered a sign of a healthy heart. People with an ejection fraction lower than 50% might be suffering from systolic heart failure. This is also termed Heart Failure with reduced ejection fraction. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. A normal range is between 52% and 72% for males and between 54% and 74% for females. An ejection fraction that’s higher or lower may be a sign of heart failure or an underlying heart.
40 to 55% – Below normal heart function. Can indicate previous heart damage from heart attack or cardiomyopathy. Higher than 75% – Can indicate a heart condition like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a common cause of sudden cardiac arrest. Less than 40% – May confirm the diagnosis of heart failure. Many doctors consider a normal ejection fraction to be 55%-75%. If yours is 50% or lower, it's a sign that your heart--usually your left ventricle--may not pump out enough blood. There's a gray.
tekkit alchemical bag dupe
For an ejection fraction in the range of 50% to 55%, most of the commonly used tests, if carefully performed, are accurate within a few percentage points (e.g. 55% plus or minus 3%). With respect to the lower limit of “normal” LVEF, it is important to remember that even at rest, the LV pumps a slightly different amount of blood in every beat. In general LVEF ≥ 55% is considered “normal” by guidelines, with a low normal designation for LVEF 50-55%. We assess the prognosis of participants with low normal LVEF in the Multi Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. All participants were asymptomatic and had no known clinical CVD at baseline. Methods and Results. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).

mildly reduced Lv systolic function
celine chain sunglasses fake
$30.99
lv ejection fraction 55|mildly reduced Lv systolic function