lv wall segments | 17 segments of left ventricle lv wall segments Wall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in . Highscore game; Bubble Shooter. Number of players: 173 Highscore game; Car Logo Puzle. Number of players: 95 Highscore game; Mah Jongg. Number of players: 26 Highscore game; Mahjongg Alchemy. Number of players: 10 .
0 · myocardial wall segments
1 · lv wall thickness echo
2 · left ventricular wall segments
3 · left ventricular wall segment model
4 · how to assess lv function
5 · coronary artery wall segments
6 · apical 4 chamber wall segments
7 · 17 segments of left ventricle
I've upgraded my crystal pump to level 4, and the requirements for level 5 are 2.5k crystals, however, at level 4 I can only hold 1k crystals. Am I missing something? Just browsing the shop, and the monthly pack page .
Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi .tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. The first obstacle is .Wall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the .
Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 . Obtaining four echocardiographic measures in the left ventricle — longitudinal shortening, anterior mitral-leaflet motion, thickening of wall segments, and change in the area .
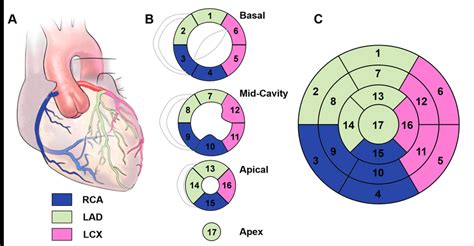
preload: end-diastolic volume (if low think -> hypovolaemia, low SVR, severe AR or MR, VSD) afterload: end-systolic wall stress (rarely used in clinical practice) LV wall thickness: .Left Ventricular Function. Myocardial Mechanics: Structure and Function of Myocardial Fibers. Ventricular Pressure-Volume Relationship: Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & .The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as .
These 17 segments can be arranged as a polar (bull’s-eye) plot with the apex in the center, the four apical segments as the first ring, the six mid-cavity segments as the second ring, and the six basal segments as the outer ring (Figure 2).Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to .
tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. The first obstacle is how to best define risk. The cutoffs suggested for the same param-eter vary broadly for different risks in different patient populationsWall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in contractile function. Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2). Obtaining four echocardiographic measures in the left ventricle — longitudinal shortening, anterior mitral-leaflet motion, thickening of wall segments, and change in the area of the cavity . preload: end-diastolic volume (if low think -> hypovolaemia, low SVR, severe AR or MR, VSD) afterload: end-systolic wall stress (rarely used in clinical practice) LV wall thickness: > 1.5cm = LVH, < 0.6cm = LV thinning. Regional Function. 16 segments. contractility: grades.
Left Ventricular Function. Myocardial Mechanics: Structure and Function of Myocardial Fibers. Ventricular Pressure-Volume Relationship: Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank-Starling’s law. Assessing left ventricular systolic function.The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1).These 17 segments can be arranged as a polar (bull’s-eye) plot with the apex in the center, the four apical segments as the first ring, the six mid-cavity segments as the second ring, and the six basal segments as the outer ring (Figure 2).Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to .
tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. The first obstacle is how to best define risk. The cutoffs suggested for the same param-eter vary broadly for different risks in different patient populations
Wall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in contractile function. Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2). Obtaining four echocardiographic measures in the left ventricle — longitudinal shortening, anterior mitral-leaflet motion, thickening of wall segments, and change in the area of the cavity . preload: end-diastolic volume (if low think -> hypovolaemia, low SVR, severe AR or MR, VSD) afterload: end-systolic wall stress (rarely used in clinical practice) LV wall thickness: > 1.5cm = LVH, < 0.6cm = LV thinning. Regional Function. 16 segments. contractility: grades.
myocardial wall segments
Left Ventricular Function. Myocardial Mechanics: Structure and Function of Myocardial Fibers. Ventricular Pressure-Volume Relationship: Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank-Starling’s law. Assessing left ventricular systolic function.
louis vuitton mens shawl
louis vuitton jacket for mens
Carbuzz.lv lietotu auto tirdzniecība klientiem piedāvā plašu auto klāstu, kurā atrodamas gan kompaktās, gan biznesa klases automašīnas par saprātīgām cenām, kā arī ar izdevīgiem nosacījumiem, izvēloties operatīvo. Parakstot operatīvā maksājuma līgumu, klientiem piedāvājam dažādus bonusus.
lv wall segments|17 segments of left ventricle