lv walls | Lv wall motion abnormalities lv walls Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the . 1. The Silhouette. The first thing you should notice when it comes to a fake bag is an imperfect silhouette. Red flags include a bag that is slouching, creased, or has unnatural proportions, meaning it probably is a fake.
0 · reasons for left ventricular hypertrophy
1 · normal Lv wall thickness
2 · myocardial wall
3 · lvh with repolarization abnormalities
4 · increased Lv wall thickness
5 · Lv wall thickness on echo
6 · Lv wall thickness normal values
7 · Lv wall motion abnormalities
Mask shape; Monogram pattern on lens and strap; Monogram Flower aeration holes on top and bottom; Louis Vuitton signature on front; Anti-fog, anti-scratch, hydrophobic lenses; Adjustable strap; Triple-layer foam; Storage case with pouch; Additional lens included; Transmittance :Z104; UV Protection :100%; Filter Category :S3
Segments of the left ventricle. Based on anatomical landmarks and autopsy studies (Edwards et al), the left ventricle is divided into three equal parts along .
Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the .
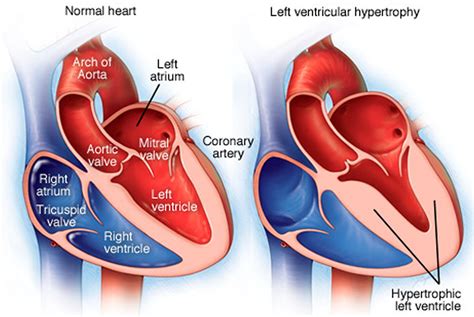
Segments of the left ventricle. Based on anatomical landmarks and autopsy studies (Edwards et al), the left ventricle is divided into three equal parts along the long axis of the ventricle. This creates three circular sections of the left ventricle named basal, mid-cavity, and apical. Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2). Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. The most common cause is .
Assessment of LV function remains the most common reason for cardiac imaging because of its powerful ability to predict morbidity and mortality. Current routine methods of quantifying LV function (with LVEF) is not without limitations.Electronic calipers should be positioned on the interface between myocardial wall and cavity, and the interface between wall and pericardium. Perform at end-diastole (previously defined) perpendicular to the long axis of the LV, at or immediately below the level of . Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography. This method utilizes the Devereux and Reichek .
reasons for left ventricular hypertrophy
Each of the following echo parameters are discussed and updated in turn: left ventricular linear dimensions and LV mass; left ventricular volumes; left ventricular ejection fraction; left atrial size; right heart parameters; aortic dimensions; and tissue Doppler imaging.Wall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in contractile function. Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of .The volume-based measurement of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is fundamentally different from direct measurement of myocardial motion by tissue Doppler imaging and myocardial deformation, and the reliability and precision of these measurements are also different.
normal Lv wall thickness
Segments of the left ventricle. Based on anatomical landmarks and autopsy studies (Edwards et al), the left ventricle is divided into three equal parts along the long axis of the ventricle. This creates three circular sections of the left ventricle named basal, mid-cavity, and apical. Recently, the consensus of the American Heart Association (AHA) 21 divided the LV into 4 walls: septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior; in turn, the 4 walls were divided into 17 segments: 6 basal, 6 mid, 4 apical, and 1 segment being the apex (Figure 2).
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. The most common cause is .Assessment of LV function remains the most common reason for cardiac imaging because of its powerful ability to predict morbidity and mortality. Current routine methods of quantifying LV function (with LVEF) is not without limitations.
Electronic calipers should be positioned on the interface between myocardial wall and cavity, and the interface between wall and pericardium. Perform at end-diastole (previously defined) perpendicular to the long axis of the LV, at or immediately below the level of . Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. Good measurements are essential and may have implications for therapy. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The first and most commonly used echocardiography method of LVM estimation is the linear method, which uses end-diastolic linear measurements of the interventricular septum (IVSd), LV inferolateral wall thickness, and LV internal diameter derived from 2D-guided M-mode or direct 2D echocardiography. This method utilizes the Devereux and Reichek .
Each of the following echo parameters are discussed and updated in turn: left ventricular linear dimensions and LV mass; left ventricular volumes; left ventricular ejection fraction; left atrial size; right heart parameters; aortic dimensions; and tissue Doppler imaging.Wall motion is assessed in each segment of the left ventricle (Figure 1; refer to Segments of the Left Ventricle). Regional wall motion abnormalities are defined as regional abnormalities in contractile function. Ischemic heart disease is the most common cause of .
rolex oyster perpetual datejust presidential 2005
myocardial wall
ESO: Jewelry Crafting Tutorial (Where to get Each Jewelry Trait and Level Your Skill Line Fast) - YouTube. Rudy Vision. 1.08K subscribers. 121. 6K views 2 years .
lv walls|Lv wall motion abnormalities